Info Englisch
To prepare for the impacts of the escalating political and economic crisis in Sudan, the Foreign Office in Berlin has invited key international researchers on Sudan, representatives from German and UK ministries, representatives from thinktanks, and representatives from international NGOs to discuss under Chatham House rules about ways to address the Current Dynamics in Sudan, the Future of the International and Regional Interventions in Darfur, and the Regional Dynamics of Sudan. Professor Karl Wohlmuth gave a presentation on Sudan’s economic problems and perspectives, highlighting the internal economic problems and the cross-border issues which are affecting the development of the country (see the Presentation on Sudan by Karl Wohlmuth). Main emphasis in the presentation was on the need to revise the national economic policy of Sudan towards stability, innovation and diversification and towards a more balanced and mutually beneficial cooperation with the seven neighbouring countries, especially so the South Sudan.
Professor Wohlmuth referred to the challenges and opportunities of economic and political cooperation programmes of Sudan with South Sudan which would yield high returns for the people and the economy of both countries – because of the high interdependence of the countries on oil production and oil transport issues, the economic role of the states (provinces) along the international border of Sudan and South Sudan, and the necessity to end conflicts in Sudan and in South Sudan through negotiated peace and development programmes. The end of the regime of Omar al-Bashir in Sudan may now provide a window of opportunity to start a “development-friendly” cooperation between the governments in Khartoum and Juba, and to build an alliance for peace and development along the international border between regions in Sudan and South Sudan.
Professor Karl Wohlmuth also presented his blueprint for an economic reform programme for Sudan and South Sudan as based on publications in the SERG Discussion Papers (see the links: https://www.karl-wohlmuth.de/serg_sudan_discussion_papers/ and http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/publikationen/pub-sudan.htm). Recently, Volume 20 (for 2018) of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook has brought interesting articles towards a strategy on Sudan’s science, technology and innovation (STI) policies, and on Sudan’s industry and agriculture policies. This part of the Yearbook on Sudan (Unit 2) builds a frame for a strategic reorientation of the Sudanese economy towards structural transformation, economic revitalization and diversification (see on this volume the links: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/africa/africanyearbook.htm, and: https://www.karl-wohlmuth.de/african_development_perspectives_yearbook/, and: http://www.lit-verlag.de/reihe/adpy).

In volume 20 of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook with the title “Science, Technology and Innovation Policies for Inclusive Growth in Africa - General Issues and Country Cases” major strategic and policy issues are analysed. The guiding issue is how to make Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) Policies relevant for inclusive growth strategies in Africa so that socio-economic transformation strategies will take off. Although STI polices are considered as indispensable for sustainable growth in Africa, the steps towards such policies and strategies are not yet streamlined enough. Therefore, it is necessary to learn from the successful cases of STI development in Africa and in other emerging countries.
African Development Perspectives Yearbook 2018:
On Science, Technology And Innovation Policies For Inclusive Growth In Africa
In this volume a new approach is envisaged. Based on Africa’s deep-routed structural problems, the STI policies are related to Africa’s economic transformation agenda. In a first part of Volume 20 the general issues of introducing effective STI policies are presented, based on visions, strategic plans and the requirements of functioning national innovation systems. In a second part, country case studies highlight the new approach. Specific case studies, such as for Sudan and Nigeria, are presented, as these two countries have a long history of STI development. Strategies and policies for more coherent STI policies are presented (see the Cover of volume 20: PDF 91042-4 Alabi).
Complementary to this volume is Volume 21 with the title “Science, Technology and Innovation Policies for Inclusive Growth in Africa - Human Skills Development and Country Cases”. In the first part of Volume 21 the role of human skills development for capacity building in STI systems is discussed. This is based on examples from Cameroon, Nigeria and Mauritania. In the second part the national innovation systems and STI policies of North African countries (Egypt and Tunisia) are evaluated, to assess how they can be directed towards economic transformation and inclusive growth.
With Volume 21 the African Development Perspectives Yearbook project is approaching 30 years of activity as the first volume was published in 1989 under the title “Human Dimensions of Adjustment”. In these 30 years the African Development Perspectives Yearbook has become the major annual publication in English language on Africa in Germany. Guiding principle is the inclusion of authors and editors from Africa, the publication of essays which are also readable by media people, development actors and policymakers, and the presentation of successful policies, projects and programmes which highlight that Africa can succeed in regard of its ambitions and that it can rise in growth and development.
The Research Group on African Development Perspectives has just released the International Call for Papers for Volume 22 (2020) and invites Abstracts and nominations for the position of Guest Editors (see International Call for Papers Volume 22, for the year 2020).
Invited are contributions for Volume 22 (2020) of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook with the title “Sustainable Development Goal 9 (Infrastructure, Industrialization, Innovation) and African Development – Challenges and Opportunities”. See the International Call for Papers for Volume 22 (for the calendar year 2020). The contributions should be evidence-based and policy-oriented. High academic standards are requested and will be checked by referees. Non-technical papers with deep analysis, which are readable by practitioners in development cooperation and by media people, have a high priority in the selection process. The concept of the contribution and the methodological framework of analysis should be outlined in the Abstract which is submitted to the Editors, Professor Karl Wohlmuth (Bremen) and Professor Tobias Knedlik (Fulda).
Source: United Nations
Sustainable Development Goal Nine (Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure) and African Development
Upon acceptance of the paper, the Contributors will receive Editorial Guidelines and a Template. Accepted papers will be grouped into Thematic Units, and the respective Unit Editors will contact the contributors quite regularly during the process of finalization of the paper to discuss the various drafts. The African Development Perspectives Yearbook is published since 1989 (see the link to the website of the Yearbook project: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/africa/africanyearbook.htm). The volumes 20 and 21 (for the years 2018 and 2019) were on the theme “Science, Technology and Innovation Policies for Inclusive Growth in Africa”. In 2019, the Research Group celebrates the event of 30 years of publishing the African Development Perspectives Yearbook. Each of the volumes 20 and 21 had three Thematic Units. Volume 22 will be related to the year 2020; in case of many high-quality submissions a Volume 23 for the year 2021 can be added. Guest Editors for various Thematic Units are also invited to apply. Editors of Thematic Units are also becoming automatically the status of Volume Editors. Guest Editors are responsible for a Thematic Unit with 3 – 5 contributions and an Introduction. For specific themes see the Main Issues proposed by the Editors for Volume 22 as presented in the International Call for Papers Volume 22 (2020). These proposals for themes are only examples. The Editors are open to further suggestions in the context of SDG 9..
The theme for volume 22 on “Sustainable Development Goal 9 (Infrastructure, Industrialization, Innovation) and African Development – Challenges and Opportunities” is related to the importance of Goal Nine in the context of the SDG Agenda 2030. SDG 9 is comprehensive and is focussing on “Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation”. The targets and indicators related to Sustainable Development Goal Nine focus on:
- a) developing quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure;
b) promoting inclusive and sustainable industrialization and raising significantly industry’s share of employment;
c) increasing the access of small-scale industrial and other enterprises to financial services, and facilitating their integration into value chains and markets;
d) upgrading infrastructure and retrofitting industries to make them sustainable in terms of resource-use efficiency and adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies; and
e) enhancing scientific research, upgrading the technological capabilities of industrial sectors, and encouraging innovation.
Focus in SDG 9 is also on facilitating sustainable and resilient infrastructural development, on supporting domestic technology development, research and innovation, and on increasing access to information and communication technologies.
The contributions will add to the knowledge about the role of SDG 9 for sustainable development and inclusive growth in Africa. Understanding the links to the other 16 SDGs of the Agenda 2030 is of great importance when drafting contributions for volume 22 of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook. The contributors should consider the links to, the spillovers from and the interactions with the other SDGs.
A new research and strategy paper on “Sudan in the 21st Century: Seeking Pathways Forward” was published as the number 43 in the SUDAN ECONOMY RESEARCH GROUP (SERG) DISCUSSION PAPERS series at the University of Bremen (see the link to the SERG series: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/publikationen/pub-sudan.htm). Author is Dr. Mohamed al Murtada Mustafa, Former Undersecretary of Labour, Ministry of Labour, Sudan and Former Director of ILO Offices in Harare and Cairo. The paper argues that for a successful reconstruction of the Sudanese economy five pillars are needed: education, entrepreneurship, agriculture, industry and management. These five pillars represent the main sectors and functional areas which must interact for inclusive growth to occur. Interaction depends on institutional reform and on a developmental role of the civil service. The separation of South Sudan in 2011 has fundamentally changed the situation of Sudan, and it is no longer possible to pursue uncoordinated, short-term and small-scale policy changes. Much more is needed – long-term structural strategies and deep policy changes must be implemented in Sudan. Fundamental reforms are proposed in the study and policy recommendations are presented for these five pillars.
Source: Dr. Mohamed al Murtada Mustafa, Khartoum, Sudan
The Strategic Pillars for Sudan’s Development
The author emphasizes also the fact that the Sudanese government has seen a great number of advisory and consultancy reports on economic strategies since 1956 when the country became independent. All these proposals and suggestions from donors, think tanks and international organisations were well-minded and valuable but were repetitive in content and never were implemented (neither by democratic governments nor by military regimes). Therefore, a new approach is needed by focussing on a developmental civil service and a new leadership for the country which is based on a broader group of policy actors – coming from all regions of the Sudan, from representative political circles and from significant parts of the civil society. Such an approach is formulated in the new SERG study. Professor Karl Wohlmuth from the University of Bremen has peer-reviewed and re-edited the paper by Dr. Murtada. It will also be circulated in Arabic language by the author.
The new volume of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook – number 20 for the year 2018 – has also a strong strategic focus on Sudan; emphasis is on the strengthening of the National Innovation System (NIS) and the Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) Policies of Sudan (issue one), on developing new policies to support innovative industrial enterprises (issue two), on attracting foreign enterprises and stimulating the technology transfer to domestic firms (issue three), and on increasing the yield in agriculture through R&D and appropriate dissemination of research results to the farming sector (issue four). Over the years the African Development Perspectives Yearbook has published regularly on Sudan and South Sudan and so has participated actively to the discussion on new development strategies for these countries (see the link to the Yearbook editions: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/africa/africanyearbook.htm). The research on Sudan by the SERG is summarized in the report on Sudan Studies in Bremen (see the link to number 38 on “Sudan Studies in Bremen 1979-2011”: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/publikationen/pub-sudan.htm). Most of the papers published by the SERG have a focus on strategies and policies to advance structural change in Sudan (and in South Sudan).

Professor Karl Wohlmuth gave a Keynote Lecture on “Transport Infrastructure and Regional Integration in Africa – A Neglected Link” at the second “Aviation in Africa” International Workshop which was organized in June 2018 by the Institute for Transport and Development (ITD) of the Hochschule Bremen (City University of Applied Sciences Bremen) on behalf of the international scientific organization GARS (German Aviation Research Society). Professor Wohlmuth emphasized in his lecture the following themes: Scoping the neglected link of transport infrastructure and regional integration; New Initiatives to link Infrastructure, Continental and Regional Development in Africa; Transformative Regional Integration and Infrastructure Development in Africa; The “Infrastructure State”, Regional Integration and Aviation Development in Africa; and Conclusions –Way Forward in Africa. More than hundred experts on aviation and development participated at the three days meeting in Bremen (see the PDF Programme and the PDF Power Point Presentation).

Professor Karl Wohlmuth speaks about “Transport Infrastructure and Regional Integration in Africa”

Professor Deusdedit Rwehumbiza from the University of Dar es Salaam speaks about “Perspectives of regional integration in East Africa”

Participants (left Conference Organizer Professor Hans-Martin Niemeier from the ITD) listen to the lecture of Professor Hans-Heinrich Bass about “Monetary Integration in East Africa”
Professor Wohlmuth argued in his lecture that a new approach towards transformative regional integration is needed for Africa to overcome the bottleneck factors which impede structural change in Africa. Not trade liberalisation is the key priority issue of regional integration, but structural transformation between and within economic sectors. This “transformative regional integration approach” contrasts with the “linear regional integration model” which was inherited in Africa from the European integration process. Also, it was strongly emphasized that transport infrastructure development is biased in Africa as roads construction (within the countries and at cross-border level) is still the key transport sector development business. Other transport modes, like railways, aviation, waterways and rivers, and ocean shipping, are still neglected. But most seriously, the mobility concepts are not clarified in Africa; it is not made clear how the transport modes are really used (by producers and consumers). Huge investment projects are agreed upon in the context of national, regional and continental transport development programmes, but financing, implementation and maintenance levels are weak, and the social, commercial and economic benefits of the projects are not always made clear. The map of PIDA’s Priority Action Plan (see below) shows how neglected other transport modes than roads (along the Corridors and the Trans African Highways routes) are and will be until 2040.
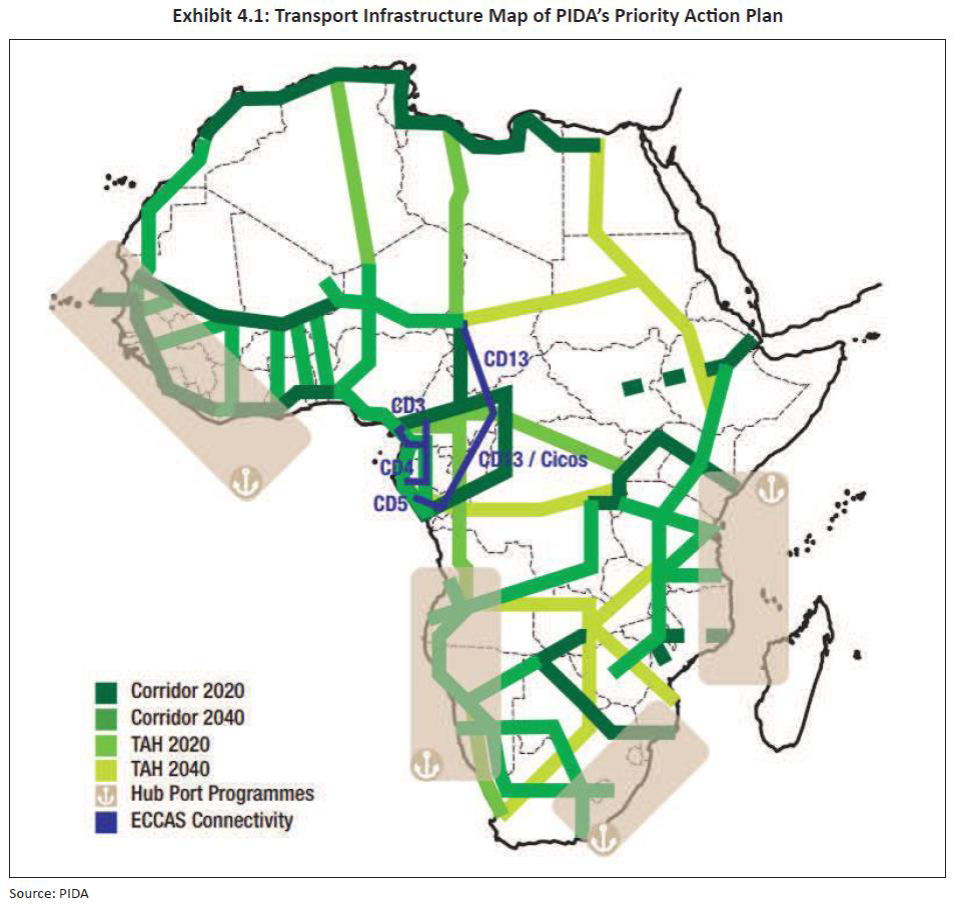
From: Export-Import Bank of India, Connecting Africa: Role of Transport Infrastructure, March 2018, p.42
Note: PIDA/Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa
Aviation has huge developmental advantages for Africa, but this transport sub-sector is still neglected in all decision-making processes, at national, regional and continental African political and governance levels. The observed progress of Africa in terms of ICT (Information and Communication Technology) and STI (Science, Technology and Innovation) development indicators gives hope and will facilitate the build-up of an aviation infrastructure. Aviation has huge effects in Africa on employment, industrialization, technological development, skills and human resources development, regional development, export development, mobility of people, goods and ideas, and especially on the opening of economies for trade, investment, technological innovation and skilled migration. The proposed publication project for volume 22 of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook on “Sustainable Development Goal 9 (Infrastructure, Industrialization and Innovation) and African Development – Challenges and Opportunities” will consider the issues of a more balanced transport infrastructure in Africa as a base for a broad industrialization advance and the speeding-up of innovation processes in African firms (see PDF International Call for Papers for Volume 22, 2020). Members of GARS and other experts on aviation in Africa are invited to submit their Abstracts to the Editors of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook (see the link to the Yearbook programme: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/africa/about.htm).
Professor Karl Wohlmuth has given advice to the Promotions Committee of the Federal University Of Technology in Akura, Nigeria. The Promotions Committee is responsible for the appointment of Professors and Associate Professors. Professor Wohlmuth was asked to evaluate candidates on the basis of their publications and overall qualifications for the position in question. It is a sophisticated multi-stages system of evaluation for the promotion to the rank of a Professor and an Associate Professor. Karl Wohlmuth was invited for this function by the Vice-President of the University and by the Head (Secretary) of the Promotions Committee. The Federal University of Technology is a leading University in Nigeria.
Also, Professor Wohlmuth has advised the Promotions Committees of the University of Khartoum (Sudan) and of the University of Juba (South Sudan) concerning appointments to Full Professorship. The University of Khartoum is on the way of reorganizing and strengthening its academic profile to regain the leading position which it had after independence among African universities. The University of Juba, as well as other universities in South Sudan, are still suffering because of the civil war in the country and the serious governance problems.
Professor Wohlmuth was also active as a reviewer of manuscripts, book proposals and articles for peer-reviewed journals. The Canadian Journal of Development Studies asked him to review manuscripts. This journal is now a leading journal on development studies in North America. The UNU-WIDER Institute in Helsinki asked Professor Wohlmuth to review a contribution for an international journal. UNU-WIDER is the globally leading institute for development research. Professor Wohlmuth was also active for the Journal Of International Development, for the journal Comparative Economic Studies, and for various African journals. Again, Professor Wohlmuth was asked to review proposals for book publications for the Economics Book Editions programme of Routledge Publishers.
Professor Wohlmuth was invited to advise a leading German multinational on issues of Customer Assessment to Optimize Business Models in Africa. As there are increasing business relations with Africa, the role of different groups of customers (by size, sector, and country) is becoming more and more relevant. It is therefore important to optimize the business models in Africa accordingly. A preparatory group of the German multinational company is involved in writing the first draft of the assessment.
Professor Wohlmuth has given advice and was peer-reviewing a Strategy Document on Revitalizing Sudan which was written by Dr. Murtada Mustafa. The Strategy Document is emphasizing five core pillars (Education, Entrepreneurship, Agriculture, Industry, and Management/Civil Service), which are considered as the basis of a new development strategy for Sudan. Dr. Murtada Mustafa was the first permanent Undersecretary of Labour in the government of Sudan. He has also had various leading functions in the International Labour Office (in Geneva, Harare, Cairo, and Khartoum). The Strategy Document will also be published in the Sudan Economy Research Group (SERG) Discussion Papers, and it will be circulated to policymakers inside and outside of Sudan. It will be published in English and in Arabic languages.
Professor Wohlmuth is also supporting and advising two Guest Researchers at the Faculty of Economics and Business Studies, University of Bremen: The agricultural economist Professor Reuben A. Alabi, Department Of Agricultural Economics, Ambrose Alli University, Ekpoma, Nigeria is in Bremen for the period 2015-2018, and the international economist Professor Chunji Yun from the Faculty of Economics, Seinan Gakuin University, Fukuoka-City, Japan is in Bremen for the period September 2017 to August 2018. For both researchers this is a further stay for research programmes, in cooperation with Professor Wohlmuth, at the University of Bremen and at IWIM. Both researchers have published in the various IWIM Publications Series. Further publications are expected from this research period.
Professor Alabi is doing researches on waste management and related value chains in Nigeria (comparing such value chains with the ones in Germany) and on aspects of the agricultural transformation in Nigeria. He is also these months working as a research fellow at the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in Washington D. C. in their African Department to do research and to give advice on the E-wallet fertilizer subsidy scheme which was introduced in Nigeria by Akinwumi A. Adesina, at that time the Nigerian agriculture minister who is now the President of the African Development Bank in Abidjan. It is the purpose of the assignment to the IMF to look at the possibilities of a wider use of the Nigerian E-wallet fertilizer subsidy scheme in other African countries. Professor Alabi and Professor Wohlmuth cooperate in Bremen on editions of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook concerning aspects of Nigeria’s economic and agricultural transformation. Most recently, Unit 2 of Volume 20 (a Unit is a collection of essays for a specific theme, introduced by the editors of the Unit) was finalized on “Science, Technology and Innovation Policies for Agricultural Transformation in Nigeria”. A strategy was outlined on the basis of the Unit 2 by Professors Alabi and Wohlmuth.
The researches by Professor Chunji Yun centre on the European integration process. He is interested in the fact that the European Union (EU) has 28 (later after Brexit 27) employment regimes and labour policies, so that cross-border investments by firms through global and regional value chains have implications for the national employment regimes and the still national labour markets. He investigates the implications of cross-border investments on nationally organized labour markets for two sectors (automobiles and electronics). He will analyse the different sectoral structures of the value chains which are demanding different types of labour by function at different levels of skills and at different places; these cross-border investments and value chains are then leading to quite different labour market outcomes. He concentrates in his research work on the cross-border investments of German companies in the Visegrad countries to study the repercussions of the changing value chains on the national labour markets and the national labour policies in Germany and in the four Visegrad countries. Because of the fact that Bremen is a centre of production networks, such as for automobiles and automotive parts, there is also the possibility for Professor Yun to visit production sites in Bremen. Professor Wohlmuth and Professor Chun have discussed the first research report in December 2017; the second research report is due in February 2018 for a further intensive discussion and review.
Professors Hans-Heinrich Bass, Robert Kappel and Karl Wohlmuth were invited by the FES Tunis to speak at the workshop “Alternative Economy and Social Justice”, 14-15 September 2017, about the future of labour in the MENA region. The focus on the first day was on Employment and Alternative Sectors: Green Economy, Digital Economy, as well as Social and Solidarity Economy. It was expected by the organizers that the experts give concrete recommendations and suggestions on the role of the civil society – more precisely the trade unions - in order to preserve labour rights and to warrant the sustainability of jobs within these new sectors of an alternative economy. The second day was reserved for a common meeting with the regional projects “Climate and Energy”, “For Socially Just Development” and the “Regional Trade Union Project”.
It was planned for the first day to have an expert debate on the subject of new opportunities and challenges of the transformation of the labour market in the context of the newly emerging three sectors in the MENA Region. In particular, the labour market implications of the Green Economy, the Digital Economy, and the Social and Solidarity Economy were discussed. The three German economists were invited because of their collaboration with the FES on a study to analyse the starting points for an employment strategy for Tunisia (see the PDF of the study: library.fes.de/pdf-files/iez/13336.pdf, and for a download of the versions in German, Arabic, French and English languages see: https://www.fes.de/t3php/publ_int.php?&f_ABC=tunis&f_RSW=tunesien&logik=or&t_listen=x&sortierung=jab&t3titel=Tunesien). A short report about the meeting summarizes the main points of discussion (see the link: http://www.fes-mena.org/events/e/alternative-economy-and-employment/). The event was part of a larger programme of the FES for the MENA region (see on the programme “Economic Policies for Social Justice”: http://www.fes-mena.org/topics/economic-policies-for-social-justice/, and on the book as a final report with the title “Towards Socially Juist Development in the MENA Region”, to be accessed for download via PDF: library.fes.de/pdf-files/bueros/tunesien/13871.pdf).
Prominent Sudanese scientists from universities and research institutions in Sudan and at UNESCO Cairo and Professor Karl Wohlmuth from the University of Bremen are launching a new strategy for a transition of Sudan from an oil-based development path towards an agriculture-based and science-based development model. This is a part (Unit 2) of the forthcoming Volume 20 of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook on “Science, Technology and Innovation Policies for Inclusive Growth in Africa. General Issues and Country Cases”. Professor Dr. Samia Satti Osman Mohamed Nour and Professor Karl Wohlmuth contributed an Introductory Essay to the theme under the title: “Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) Policies for Sudan’s Economic Revitalization - An Introduction”. The Unit 2 in Volume 20 of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook with the title: “Science, Technology and Innovation (STI) Policies for Sudan’s Economic Revitalization” has four additional essays. Professor Samia Satti Nour presents an analysis of the national innovation system (NIS) of Sudan, by focusing on three subsystems, the education institutions subsystem, the science & technology institutions subsystem, and the ICT institutions subsystem; the weaknesses of the NIS are highlighted and an agenda for action is proposed. She also presents in a second essay an analysis about innovative industrial firms in Sudan, focussing on two internationally active Sudanese conglomerates in the food industry, on two large-sized companies (belonging to the chemical and food industries) and on two medium-sized companies (belonging to the metal and textile industries). The purpose is to assess how innovative these companies really are and how they could improve their innovation performance. It is also measured by a new analytical approach how far away these companies are from the innovation frontier, and it is analysed what the government and the private sector can do to stimulate STI in the Sudanese companies.
Migdam E. Abdelgani, from the National Centre for Research (NCR), Environment, Natural Resources and Desertification Research Institute (ENDRI), and Nazar Mohamed Hassan, from the UNESCO Cairo Office, provide an essay on the impact of agricultural research on the agriculture yields in Sudan. ENDRI has recently launched the Environment and Natural Resources International Journal (ENRIJ), with volume 1 and number 1 published in 2016 (link: http://www.sudanknowledge.org/journals/enrij/); ENDRI is a key research institution in Sudan. This essay is analysing the factors which are impeding yield increases in Sudan, but this essay is also using the example of the national crops campaigns in Egypt (such as for rice production increases) as a model of large-scale testing of agricultural research results in the field.
Finally, the Unit 2 on Sudan in Volume 20 presents an analysis by Mohammed Elhaj Mustafa Ali from the University of Kassala and the Sudan International University (SIU) about knowledge spillovers from foreign investors in Sudan to local companies. Although the oil-based growth in Sudan has attracted mainly investment for the oil sector, foreign investment was also incoming to supply the growing Sudanese consumption market and to invest in agriculture and services sectors of Sudan. The essay on knowledge spillovers from foreign direct investors to domestic firms in Sudan gives also an agenda of how to stimulate technology transfers from foreign firms to domestic firms.
In the Introductory Essay by Professor Samia Satti Nour and by Professor Karl Wohlmuth also an Agenda for Reforms aimed at Economic Revitalization through STI Development is presented. The Strategy proposed has short-term to medium-term to long-term implications for reforming institutions and policies. Professor Samia Satti Nour is a prominent researcher on STI development. She recently has obtained a full professorship at Khartoum University (see the PDFs of the Inaugural Lecture/ICT Development in Sudan and the Inaugural Lecture/Academic Profile of and Awards to Professor Samia Satti Nour, as well as the PDF on the Abstract in English and in Arabic of her Springer Book ICT in Sudan). Professor Wohlmuth was invited to attend the inaugural meeting at the University of Khartoum. Professor Samia Satti Nour is adviser to the African Development Perspectives Yearbook programme for Volume 20 and Co-editor of Volume 20. Recently she has presented a Policy Note on the multiple Digital Divides in Africa for The Nordic Africa Institute (see the PDF: NAI Policy Note).
Dr. Hassan Mohamed Nazar is also Co-editor of the Volume 20 of the African Development Perspectives Yearbook. He is Senior Science and Technology Specialist for the Arab States in UNESCO’s Cairo Office since 2009. He has massively contributed to the Introductory Unit 1 for Volume 20 (together with Professor Karl Wohlmuth), and he has participated as a speaker at the Launch Event for volumes 18 and 19 of the Yearbook in Kigali, Rwanda in October 2016 at the invitation of UNECA. In the Unit 2 on Sudan for Volume 20 he contributed with an essay on the role of agricultural research for increasing agricultural yields in Sudan, an essay which was written in cooperation with Migdam E. Abdelgani. Dr. Hassan Mohamed Nazar has also established the Sudan Knowledge (SK) Platform to make the intellectual capacities of the Sudanese researchers and other experts and policymakers known more widely and to allow for a broader use of these capacities for development. The SK Platform is a strong network of researchers, policy makers, educators, consultants and employers from all parts of the world to exchange knowledge and experience and to discuss current developments and challenges. This Directory of Capacities of the Sudanese can be used to help find, support and collaborate with experts from the SK network. The Sudan Knowledge Network aims also to bring together researchers and experts from the Diaspora (see the various links: http://www.sudanknowledge.org/network/name/nazar-hassan/, and: http://www.sudanknowledge.org/network/locality/Cairo/, and: http://www.sudanknowledge.org/network/country/Egypt/).
Migdam E. Abdelgani, from the National Centre for Research (NCR), is known for his study (in cooperation with other Sudanese researchers) about “Potential Production and Application of Biofertilizers in Sudan”, published in the Pakistan Journal of Nutrition 9 (9), pp. 926-934, 2010 (link: www.sustech.edu/staff_publications/20100822070957958.pdf). These ideas are relevant for an agricultural transformation strategy which is part of the economic revitalization programme for Sudan.
Dr. Mohamed Elhaj Mustafa Ali, as the author on the essay about knowledge spillovers from foreign investors to domestic firms in Sudan, is lecturer at the University of Kassala and at the Sudan International University (link: http://www.siu-sd.com/). He is expert on foreign direct investment in Sudan and has recently published a Policy Brief on the relevant issues of foreign investment in Sudan in Bremen at the SERG/IWIM platforms (see the PDF: Mustafa Ali -Policy Brief). He has also published a Policy Brief for the Economic Research Forum (ERF) in Cairo on “Measures to Protect Poor Sudanese Households from the Risks of Catastrophic Health Expenditures” (see the PDF: PB28-Mustafa Ali).
There are intentions to continue to cooperate in the future on the most important issues of STI development for Sudan. The Sudan Economy Research Group (SERG) Discussion Paper Series is still open for researchers from Sudan to publish on these most important issues (see the links to the series: https://www.karl-wohlmuth.de/serg_sudan_discussion_papers/, and: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/publikationen/pub-sudan.htm).
The outline of a new development strategy for Sudan was prepared by Dr. Mohamed al Murtada Mustafa. Dr. Murtada was the first permanent Undersecretary for Labour in the Sudan, the Director of the African Regional Labour Administration Centre (ARLAC) for the English-speaking African countries in Harare, Zimbabwe, and then the Director of the International Labour Office in Egypt before retiring to academic and philanthropic endeavours in Khartoum. He was educated at Addis Ababa University, Harvard University, the University of Wisconsin, Northeastern University, and the International Institute for Labour Studies in Geneva. Dr. Murtada was an early collaborator of the Sudan Economy Research Group (SERG) in Bremen. He has supported the research work on Sudan in Bremen tremendously. Now he pays again tribute to his country by presenting to key policymakers the contours of a new development strategy for Sudan which is based on decades of experience as a civil service official and member of the Government of Sudan and as an employee and head of offices of the ILO with working times in Khartoum, Geneva, Harare, and Cairo. Dr. Murtada has published in IWIM publication series, such as in the SERG Discussion Paper Series, but also in the IWIM Book Series (see the link to the IWIM Homepage, Publications: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/publikationen/index.html).
The frame and the basic ideas for a new development strategy for Sudan are summarised below in the words of Dr. Murtada (taken from the Strategy Paper, which will be published as the number 43 in the SERG Discussion Paper Series, with the links: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/publikationen/pub-sudan.htm and https://www.karl-wohlmuth.de/serg_sudan_discussion_papers/):
The earliest studies by the International Labour Office (ILO) in conjunction with the Sudanese Government (Ministry of Labour) and the University of Bremen (SERG) in 1976 up to today repeat almost the same recommendations to enhance and improve the Sudanese economy. The recommendations were, just to mention some key ones: Improve infrastructure; develop industry; link agriculture to manufacturing; increase vocational and technical training; reform taxes to encourage industry and exports; support small industries, the vulnerable people, and remote regions; institute rule of law; ensure contract enforcement and transparency to encourage foreign investment; and provide for sustainable economic policies via effective institutions and a responsible macroeconomic policy formation. Whether from lack of political will, leadership, economic means, or external financial investment, the neglect of all these recommendations along with conflict, civil war and international sanctions has continued to disintegrate the development options in the Sudan. After decades of conflict and civil war, the government of Sudan now faces the burden of reconstructing the country, the society and its economy, of repatriating internally displaced persons (IDPs) and providing training and jobs for them in urban and rural areas, also to replace redundant cattle-herding livelihoods and to initiate agricultural projects for food security in depleted environments. While the discovery of oil brought revenue before the great country of the Sudan split into two republics, the oil money was not properly used to expand and to develop the economy. The agricultural sector, the industrial sector, the civil service, and the education sector deteriorated from the satisfactory state they were left in by the British at independence. Although the country since independence has presented a lot of plans and programmes, implementation was always weak or non-existent.
This strategy paper by Dr. Murtada outlines changes which are necessary to get the economy back on track in five major sectors stemming from and supporting institutional revisions: education, entrepreneurship, agriculture, industry, and management. While the short-term and the long-term solutions are outlined, the Sudanese people themselves need to pull together, to stop competing for power and land, to produce and support fresh leaders, and to begin to consider the long-term conditions of the country for the good of its own people. The Strategy Paper is structured as follows: After the Introduction (section 1) the section 2 is on Building Capacity, Growth, and Employment through Education, with Recommendations for Education. The section 3 is on Combatting Unemployment, Promoting Growth through Entrepreneurship, with Recommendations for Entrepreneurship. Section. Section 4 is on Improving Growth and Employment through Agriculture, with Recommendations for Agriculture. The section 5 is on. Growth and Employment through Industry, with Recommendations for Industry. The section 6 is on Management, by Improving Civil Service, People, Goods, and Resources, with Recommendations for Management. Section 7 is on. Results of Past Efforts and Lessons Learned. The Section 8 is Towards a New Strategy. And the final section 9 is on Conclusions, followed by References on the history of policymaking in Sudan.
Professor Karl Wohlmuth from the University of Bremen has given advice to the author during the process of finalizing the Strategy Paper and has peer-reviewed the paper. The research on Sudan and South Sudan is continuing at the University of Bremen (see the links to the websites: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/forschung/forsch-sudan.htm and: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/africa/Sudanforschung.htm).
Professor Chunji Yun, Professor since 2010 at the Division of International Economics, Department of Economics, Seinan Gakuin University, Fukuoka City, Japan is since September 2017 Guest Researcher at the Faculty of Economics and Business Studies, University of Bremen; he will stay until August 2018. He was invited by Professor Karl Wohlmuth and the Dean, Professor Jochen Zimmermann, to do researches on the theme Transforming the European Social and Economic Model in the Enlarged EU from a Viewpoint of the Production and Employment Regime (see the synopsis of the research outline below under Research Purpose,..). This is the second research visit by Professor Yun in Bremen. Ten years ago Professor Yun was research fellow at IWIM for 18 months. He has published in the IWIM book series as number 13 (Link: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/publikationen/pub-jwt.htm) on “Japan and East Asian Integration” and in the White Discussion Paper series as number 33 (Link: http://www.iwim.uni-bremen.de/publikationen/pub-white.htm) on “Production Network Development in Central/Eastern Europe and Its Consequences”. Based on these publications, Professor Yun was invited to international conferences and he was asked to submit papers for international publications. The contact between IWIM, University of Bremen and Professor Yun continued over the years.
Research Purpose, Analytical Standpoints, Previous Studies and Expected Research Results (a short summary of the Research Proposal):
With the deepening of the economic integration, and particularly since the recent Euro Crisis, there are heated debates over the social dimension of integration in Europe. The background of the discussion is if the European Union (EU) aims at an ‘Economic Europe’ or moves towards a reconstruction of a ‘Social Europe’. In this context, the research aims to analyse the transformative dynamics of economic and social models in the enlarged EU, by exploring how nationally organized employment regimes are forced to adapt to the deepening of an ‘Economic Europe’. More specifically, the national employment regimes are affected by changing cross-border production regimes which are characterized by processes of “fragmentation of production”, “global/regional production networks”, and “global value chains (GVC)”. Also, an investigation of the possibilities of reversing the ‘Race-to-the Bottom’ situation of social conditions within the EU is intended as part of the study.
The research will be carried out as mainly being based on two influential analytical perspectives, the “variety of capitalism” approach and the “global value chain” approach. The former approach has analysed various European economic and social models, focusing on the institutional complementarity among industrial relations, including collective bargaining, labour market flexibility or rigidity, the vocational training system, the financial system, and so on. This approach is also giving special attention to the interrelationships among the required skill specificity, the skill formation, employment and social protection systems, and the institutional comparative advantages of each national employment model. On the other hand, the latter approach, as a most influential analytical perspective on global manufacturing and service industries, has elaborated analyses of a cross-border division of labour featured as vertical specialization or vertical integration/disintegration. This latter approach is using a sophisticated methodology and is developing policy arguments for industrial upgrading within the hierarchical structure of the new international division of labour. And, most recently, its focal point is shifting from industrial upgrading to social upgrading/downgrading. The most important feature of the research is to figure out the interactions and/or the causal relations between GVC development within and beyond the enlarged EU and the transformation of economic and social models.
Research Outcomes by February 2018: First Research Report is available, Second Research Report is forthcoming
Professor Yun has presented a first report on his researches in December 2017. The second research report is forthcoming in February 2018.
In the first research report from December 2017 Professor Yun discusses four themes:
1. Starting Point or Background of Research (first draft)
There is a discussion about two prevailing myths. The Myth 1 is related to the Eurozone Crisis considered as being due to fiscal profligacy and being a sovereign debt crisis right from the start. The Myth 2 refers to the Eurozone Crisis as a crisis of (Unit Labour) cost competitiveness in combination with fiscal irresponsibility. These two arguments are evaluated.
2. Problematic Causal Chain of (Cost) Competitiveness, Imbalances, and Internal Devaluation (first draft)
There is a discussion of the role of the Unit Labour Cost (ULC), being considered as an a priori argument for labour market reform being inherent in the referred to competitiveness indicators. The drawbacks of the ULC analysis are presented. This is followed by a survey of recent researches on the regional imbalances in the EU.
3. The Germany-centred production network and the regional imbalances in the European Union (still work in progress)
There is a discussion on the contradictory neoclassical views on the German export surplus, then a discussion on the German position within the regional production networks (manifested by the GVCs), and finally a discussion on the changes occurring and the differences becoming visible in regard of Global Value Chain-GVC/ Global Production Network-GPN Structures.
4. Transforming the Employment Regime in terms of GVC/GPN: Germany and Visegrad (still work in progress)
The analysis starts with a discussion on social upgrading/downgrading in GVC-based development patterns, followed by an analysis of the erosion of the German Model interpreted as a Diversified Quality Production (DQP) model. Then the changes of this model are analysed, by looking at two kinds of modularization and the implications for the production networks, referring to the electronics and automotive sectors. Then for these two sectors the implications of the expanding production networks on the employment regimes are considered.
Professor Yun is doing intensively literature researches, but is also attending conferences, lectures and discussions with experts in the field. He is also considering to visit international enterprises which are located in Bremen, as these enterprises are valuable sources for information on global value chains (GVCs) and global production networks (GPNs) between Germany and the Visegrad countries. Professor Karl Wohlmuth is meeting regularly with Professor Yun for discussions of the issues. The study has high relevance also for the strategy of the German trade unions as globalization impacts differently on economic sectors in Germany.



